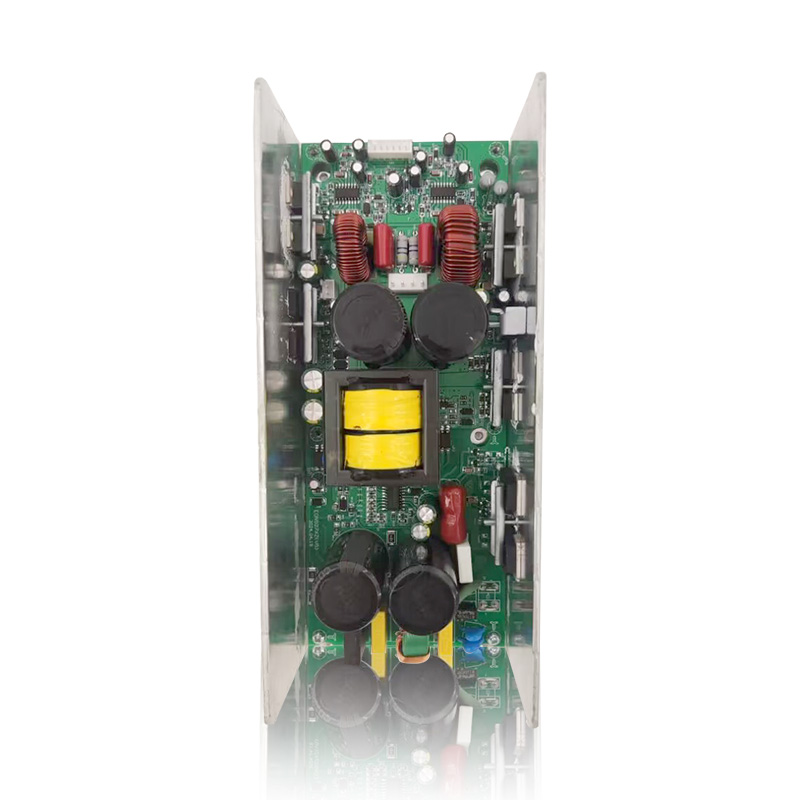
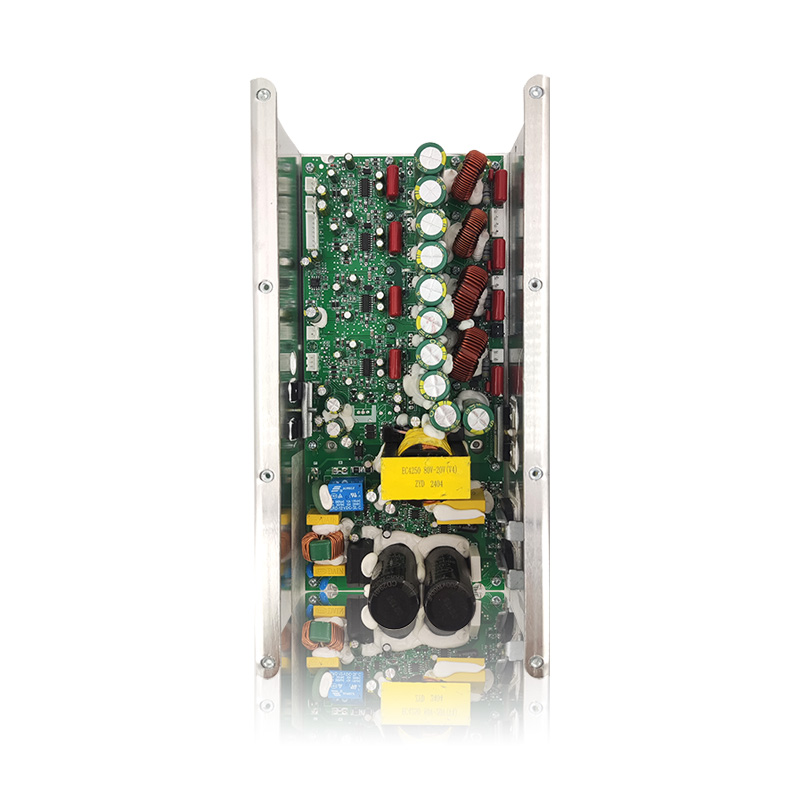
When selecting a Class H loudspeaker amplifier, factors such as sound quality, efficiency, power, heat dissipation, and stability need to be considered to ensure the equipment meets your needs (e.g., professional performances, home theaters, or recording studios). Here is a detailed selection guide:
1. Understanding the Characteristics of Class H Loudspeaker Amplifiers
Class H loudspeaker amplifiers are a high-efficiency improved version of Class AB amplifiers, featuring:
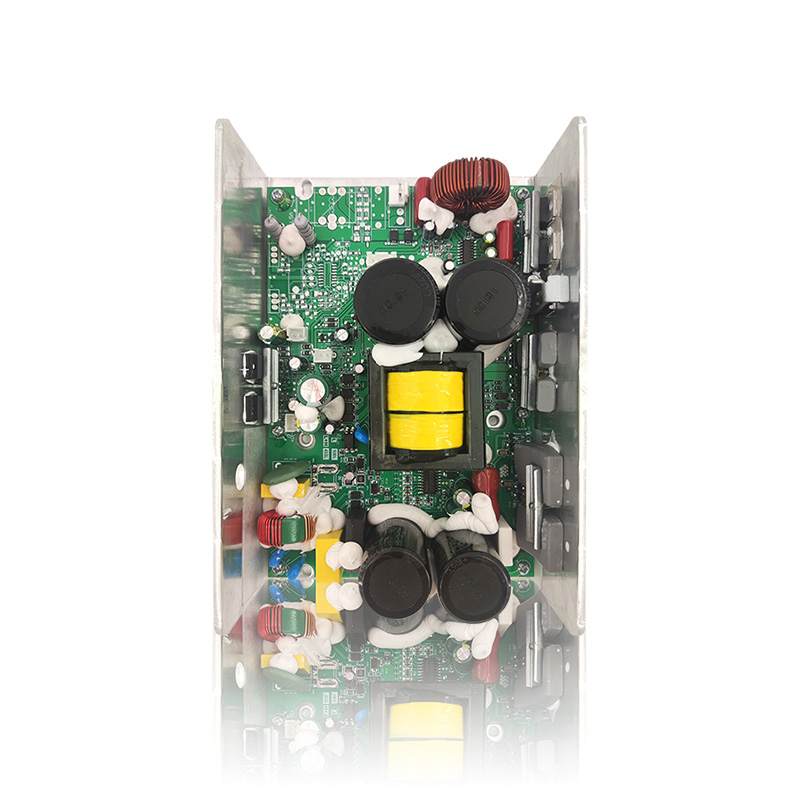
Dynamic power supply voltage adjustment: Automatically adjusts the power supply voltage according to the input signal magnitude, reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency (higher efficiency than Class AB).
Sound quality close to Class AB: Compared to Class D amplifiers, Class H amplifiers have a warmer and more natural tone, suitable for high-fidelity (Hi-Fi) applications.
Suitable for high-power scenarios: Commonly used in professional audio, stage sound reinforcement, and cinema systems.

2. Key Selection Parameters
(1) Power Matching
RMS Power (Continuous Power): Ensure the amplifier power matches the speaker's rated power (it is recommended that the amplifier power be 1.2 to 1.5 times the speaker's rated power to avoid clipping distortion). Peak power: Suitable for handling transient high dynamic signals (such as drum beats and explosions), but not for long-term reliance.
Impedance matching: Common speaker impedances are 4Ω and 8Ω; ensure the amplifier supports the corresponding load.
(2) Sound quality performance
Total harmonic distortion (THD): <0.1% is ideal; lower frequencies result in purer sound.
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR): ≥90dB (professional-grade recommendation >100dB), reducing background noise.
Frequency response: 20Hz~20kHz (covering the range of human hearing), a flat curve is better.
(3) Efficiency and heat dissipation
Class H efficiency: Typically 60%~70%, higher than Class AB (50%), but still requires good heat dissipation.
Heat dissipation design: Check if it is equipped with a large heatsink, fan (active cooling), or ventilation holes to avoid overheating and shutdown.
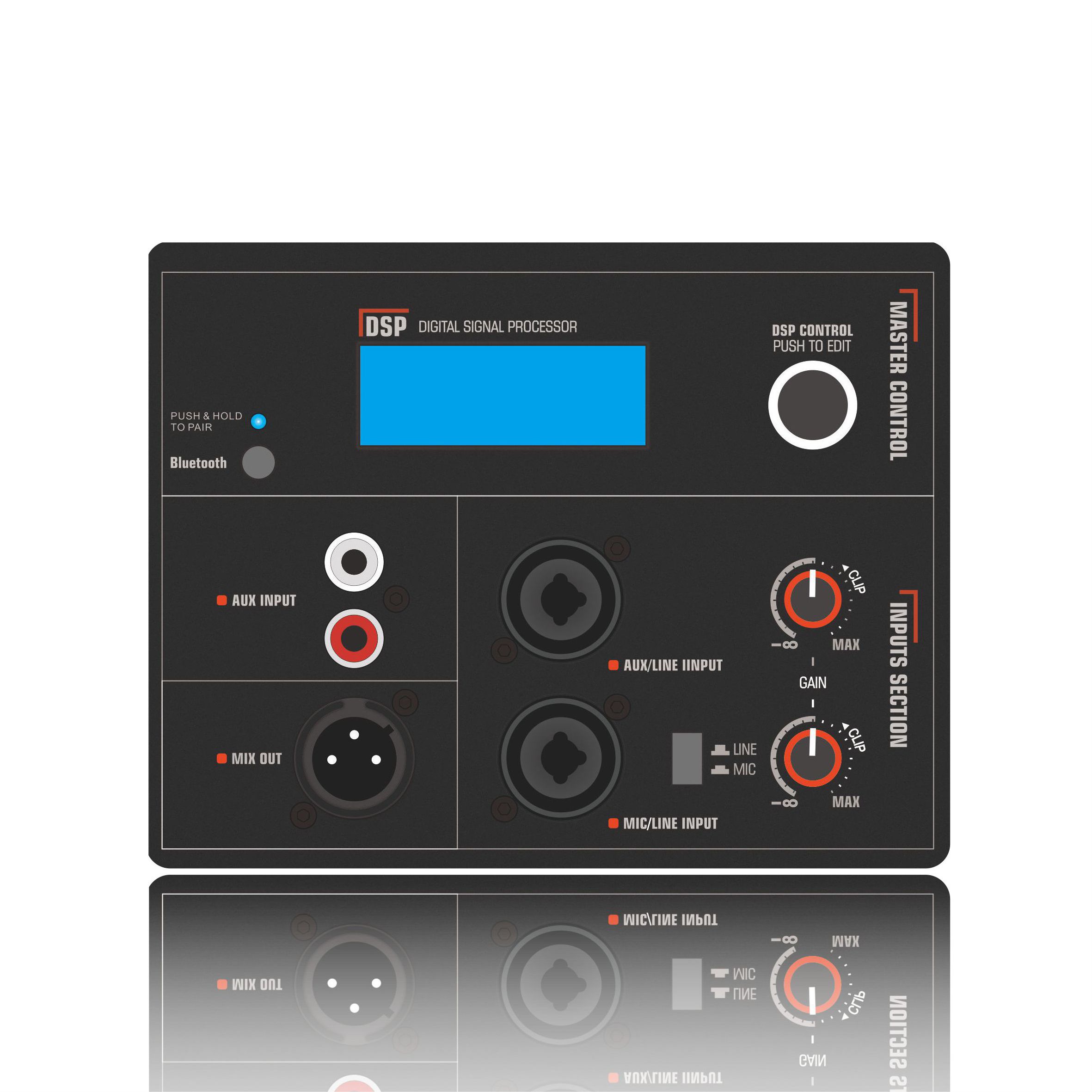
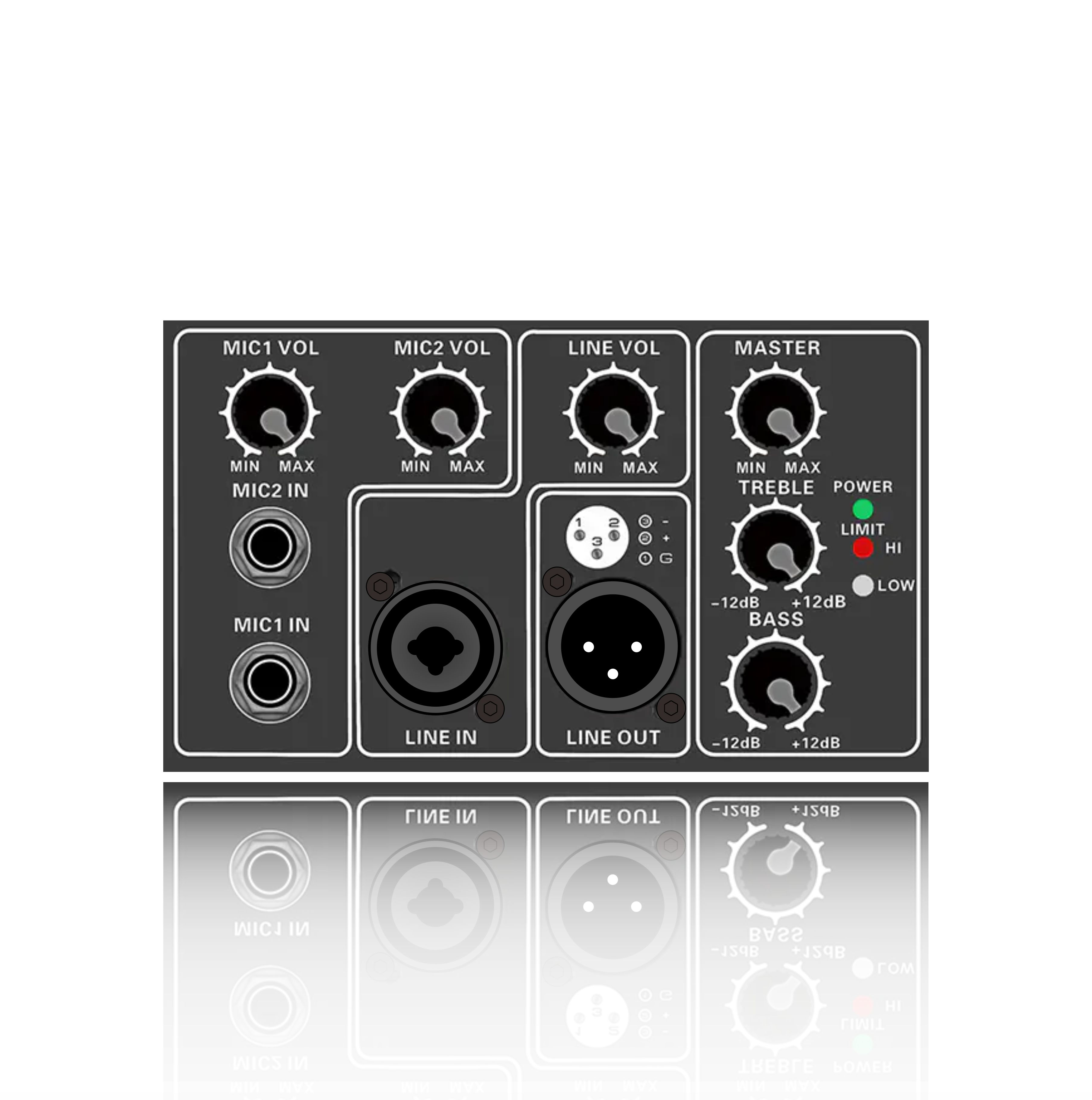
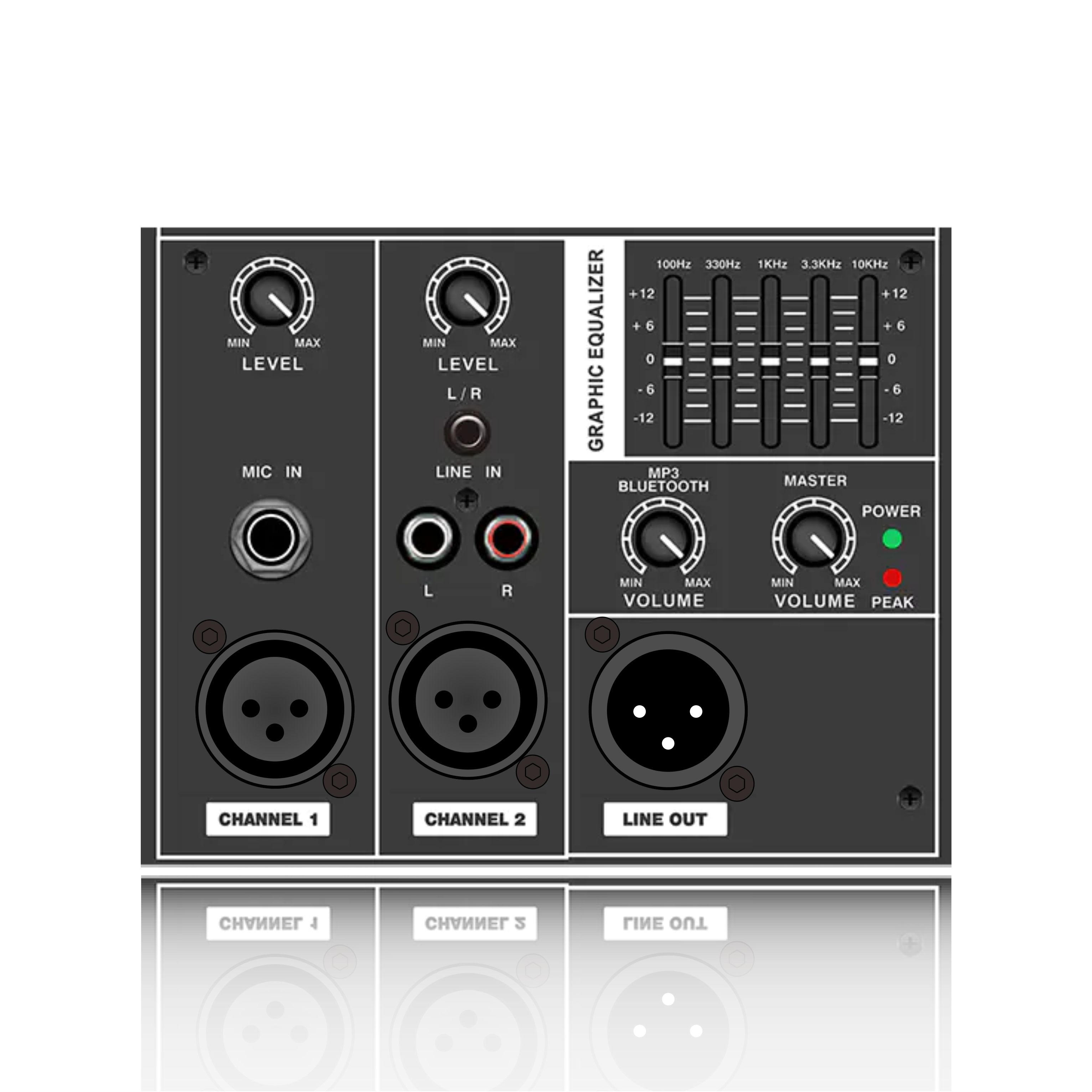
(4) Input/output interfaces
Input interfaces: XLR (balanced), RCA (unbalanced), TRS (6.35mm), ensuring compatibility with audio source devices. Output Interfaces: Binding posts (banana plug), Speakon (commonly used in professional audio), for easy connection to speakers.
(5) Protection Functions
Overload Protection (OLP): Prevents damage to the equipment due to power overload.
Short Circuit Protection (SCP): Prevents damage to the amplifier due to incorrect wiring.
Overheat Protection (OTP): Automatically reduces power or shuts down at high temperatures.
DC Protection (DC Protect): Prevents damage to the speakers due to DC output.
3. Other Considerations
Listening Comparison: Different brands have significant differences in sound quality; actual listening is recommended.
Weight and Size: High-power Class H speaker amplifiers are relatively heavy (due to heat dissipation requirements); placement space needs to be considered.
Future Upgrades: Reserve power margin to avoid future upgrades or replacements.

 English
English Español
Español 中文简体
中文简体