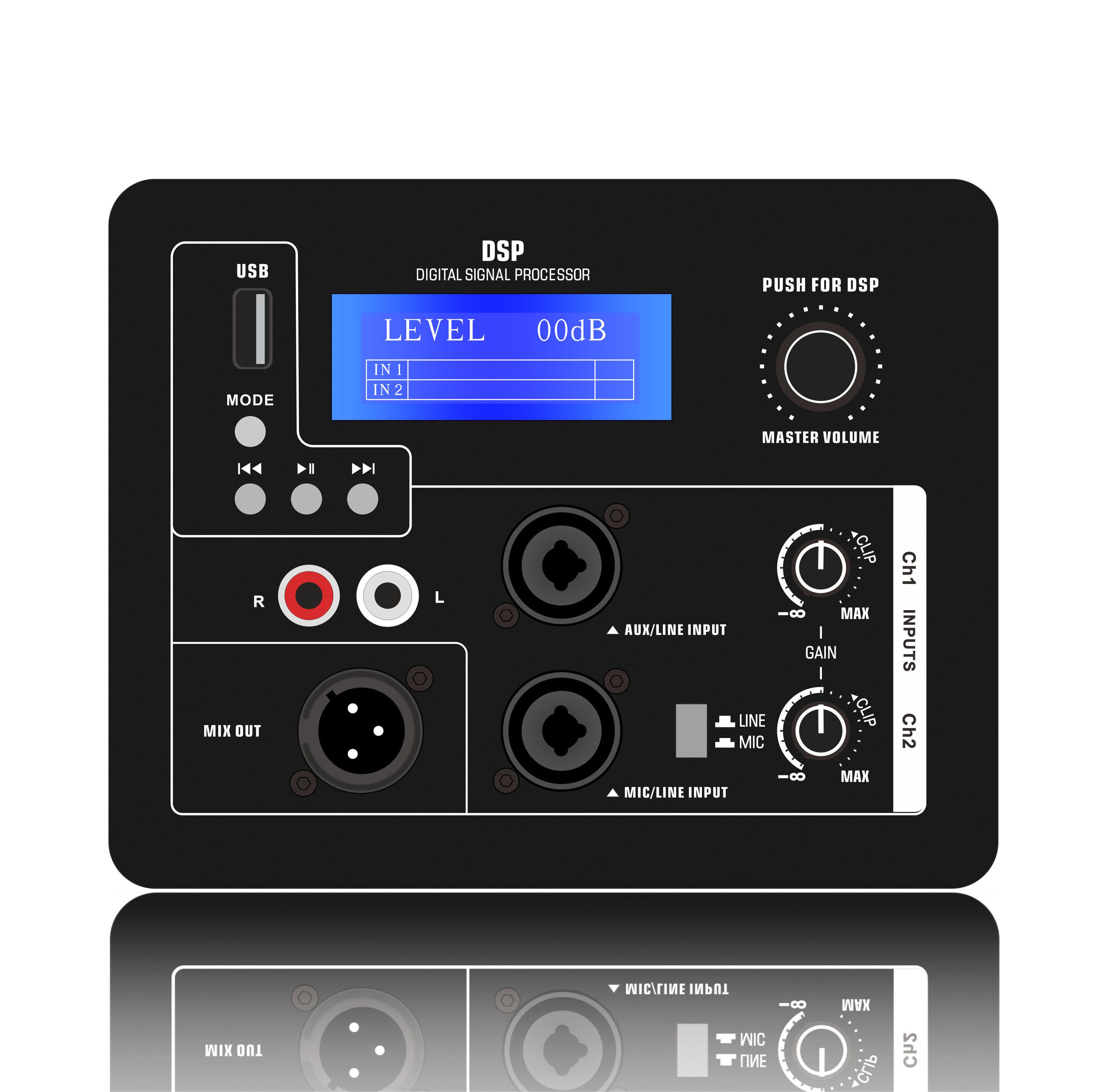
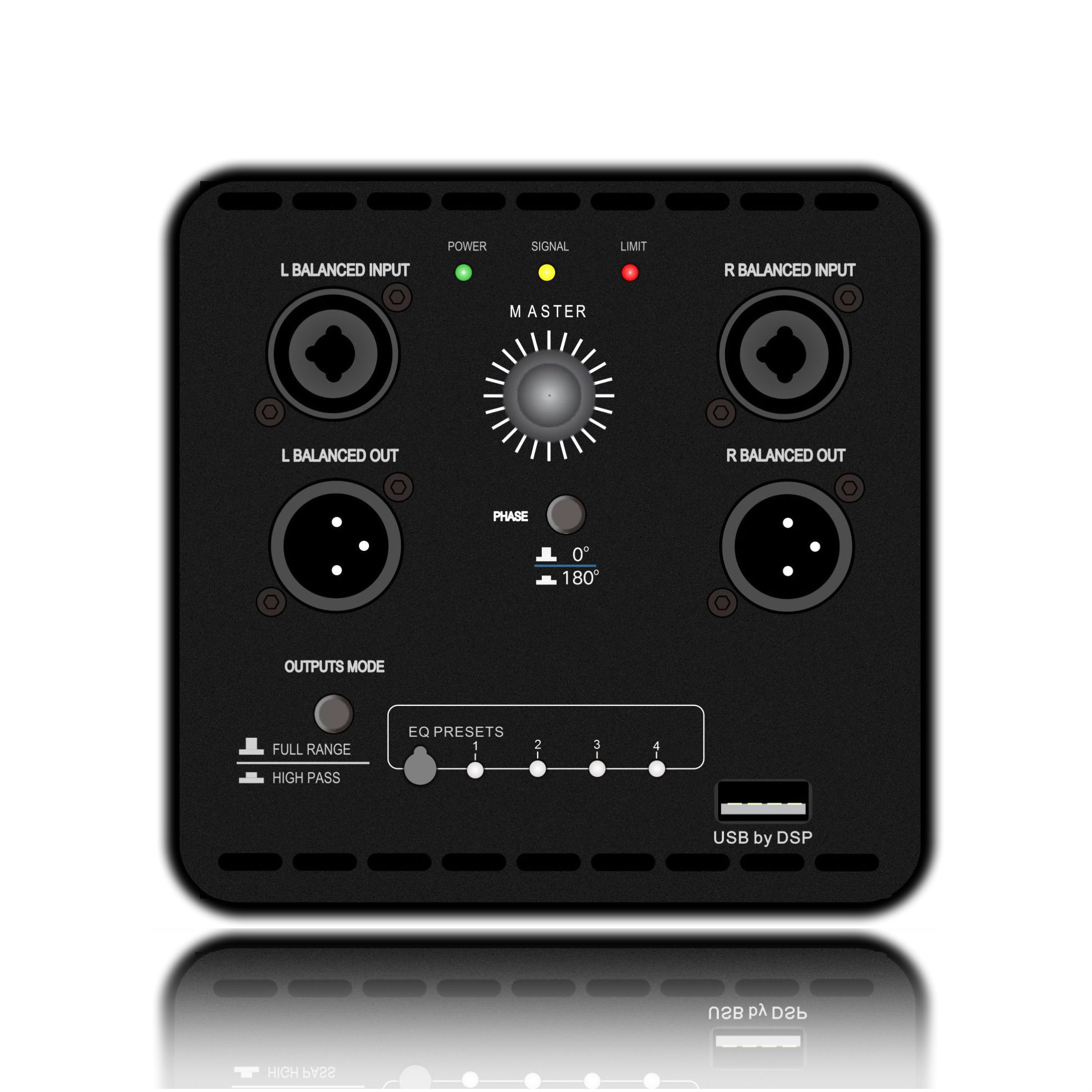
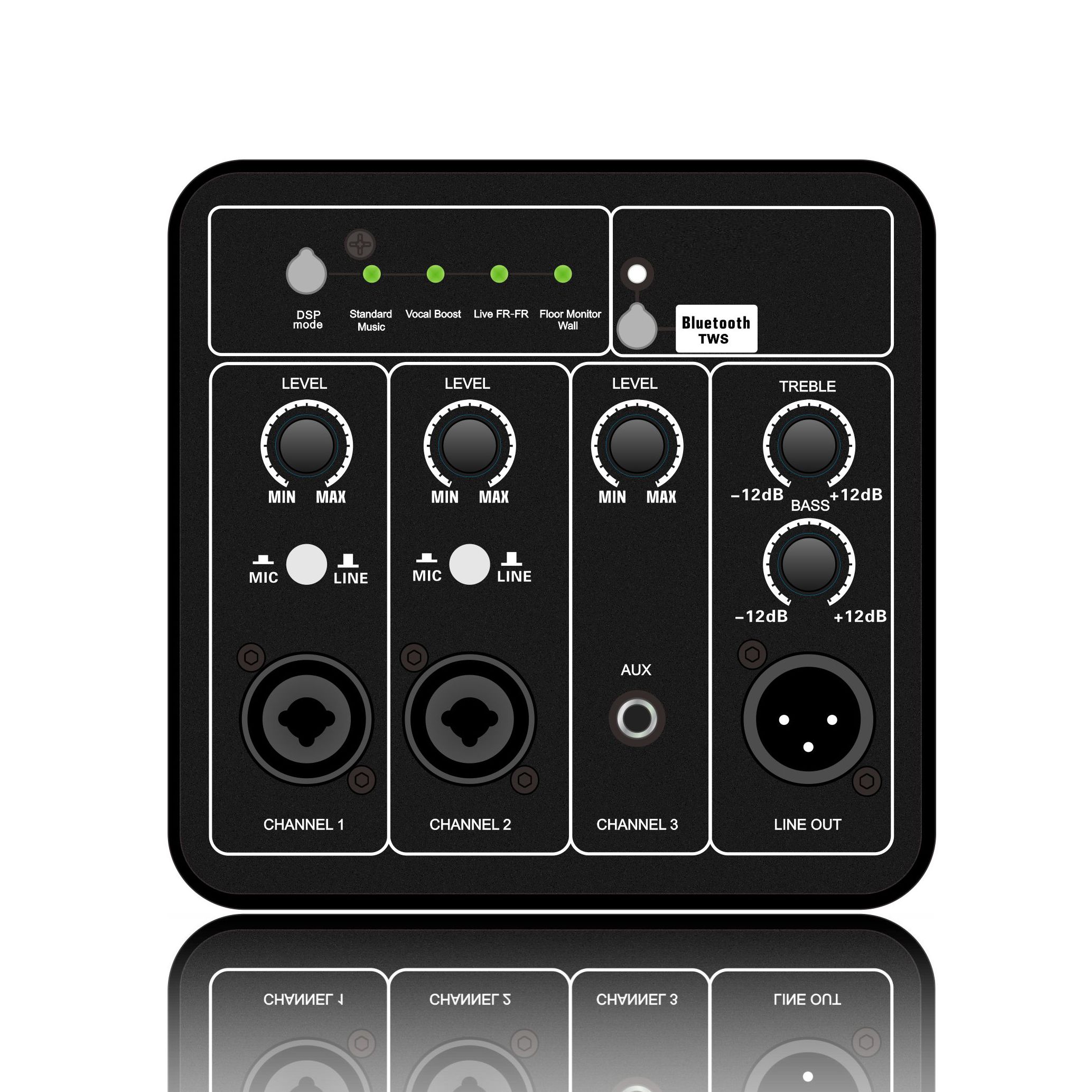
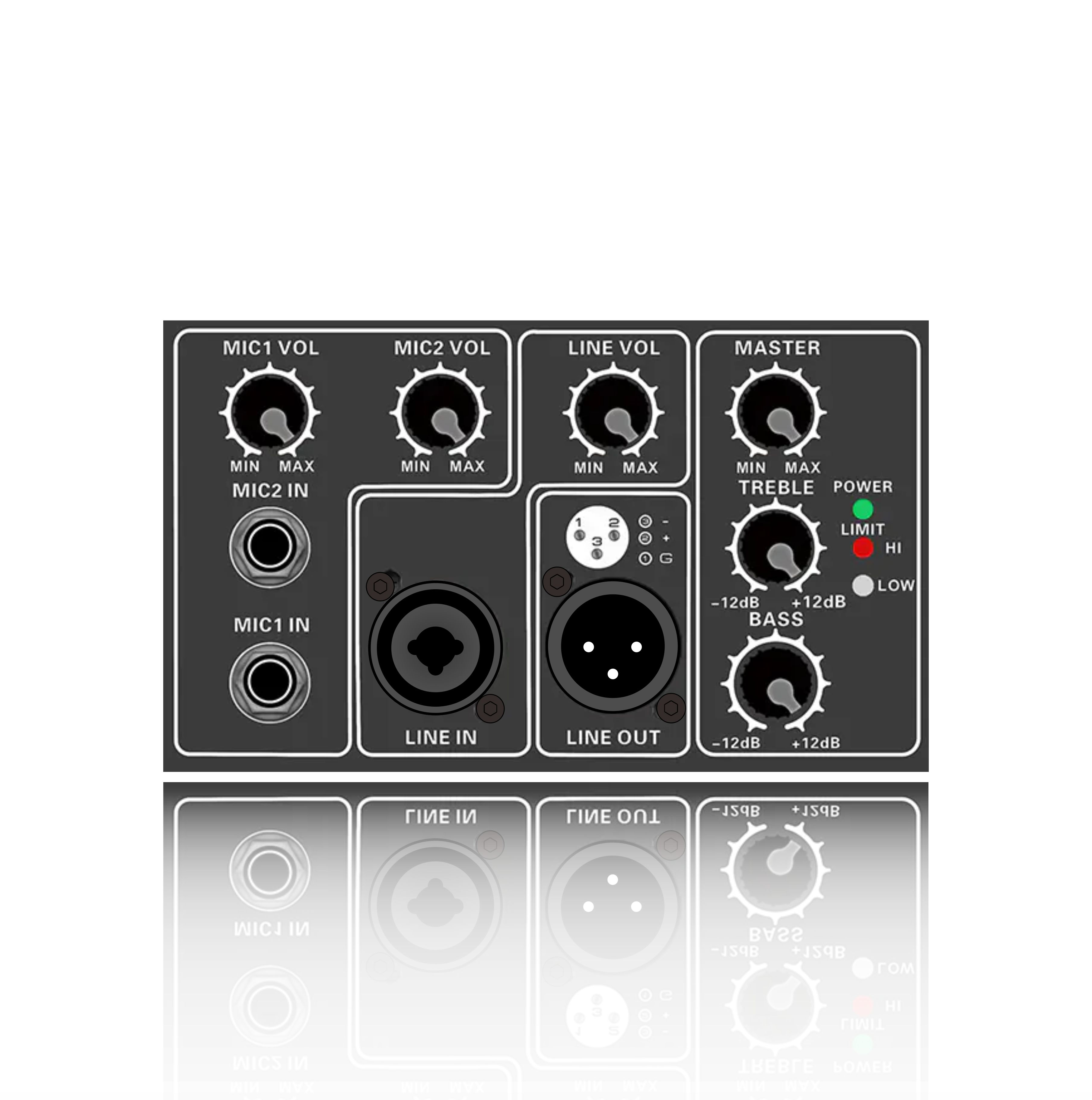
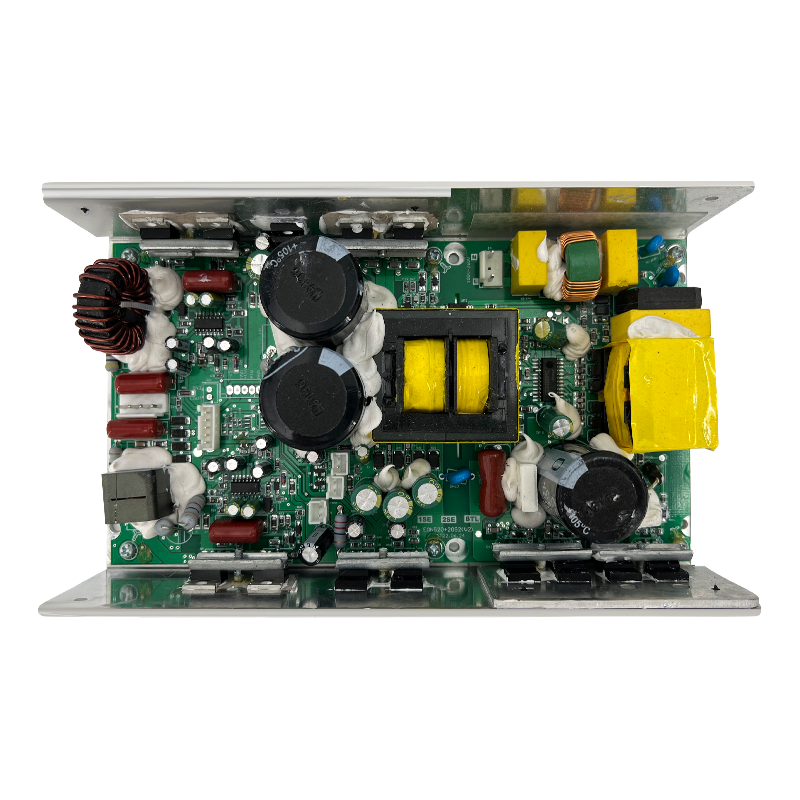
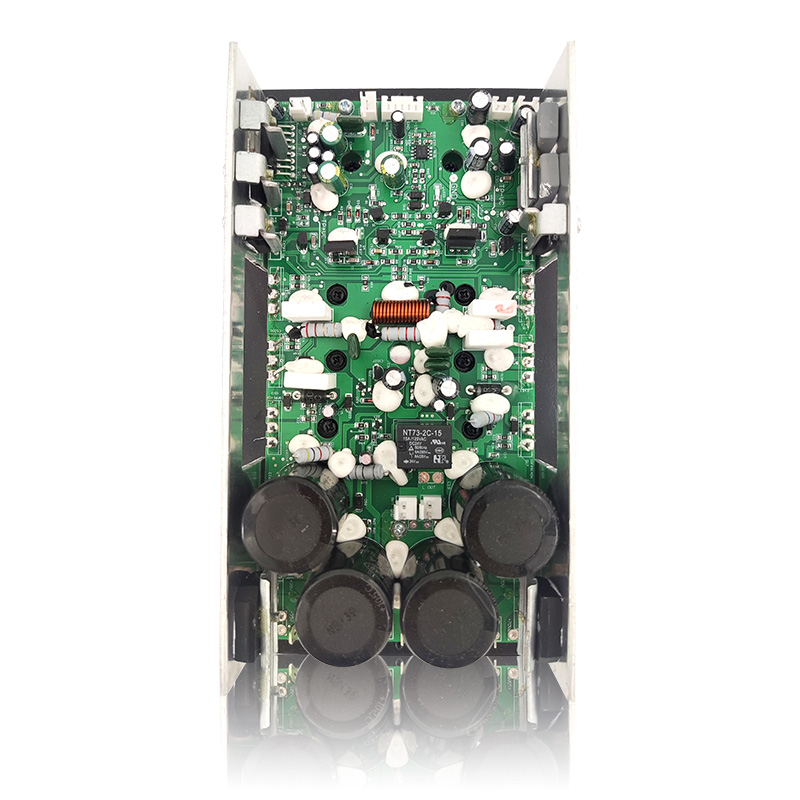
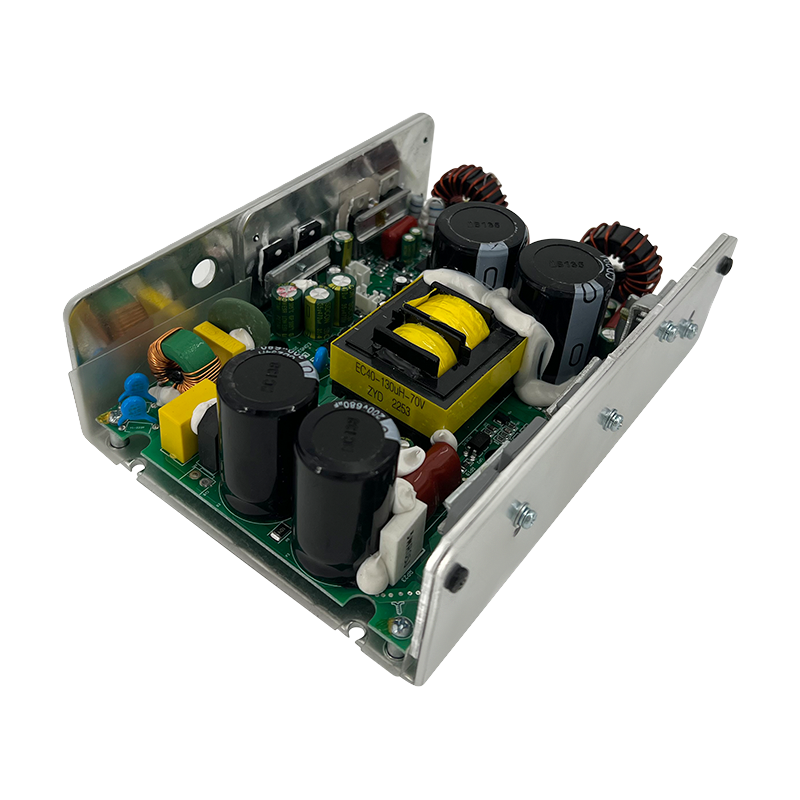
Class H Loudspeaker Amplifier is an audio power amplifier that improves efficiency by dynamically adjusting the power supply voltage. Its core design goal is to significantly reduce power consumption while ensuring sound quality. It is suitable for high-power application scenarios (such as professional audio, car audio systems, etc.).
1. Dynamic power supply voltage adjustment technology
The core innovation of Class H amplifier is to dynamically adjust the power supply voltage according to the real-time needs of the audio signal, rather than always using a fixed high voltage power supply like traditional Class AB amplifiers.
When the signal is low: use a lower power supply voltage (such as ±15V) to reduce the voltage drop (Vce) of the output stage transistor, thereby reducing power consumption.
When the signal is high: automatically switch to a higher power supply voltage (such as ±50V) to ensure sufficient output power and avoid clipping distortion.
Continuous adjustment: Some Class H designs use a continuously adjustable power supply (such as a DC-DC boost circuit) to achieve smoother voltage transitions and reduce switching noise.
Improved efficiency: Dynamic voltage allows transistors to always operate in a state close to the minimum voltage drop, with a theoretical efficiency of 70%-80%, much higher than the 50%-60% of class AB amplifiers.
2. Complementary symmetrical circuit and multi-stage power supply architecture
Complementary symmetrical output stage: Class H amplifiers usually use class AB output stage structure (common emitter pair or push-pull circuit), but realize dynamic switching through multiple power supplies.
Seamless switching technology: By predicting the audio envelope or monitoring the signal amplitude in real time, control MOSFET or relay to switch power rails to avoid transient distortion during switching.
Integrated control circuit: Modern class H chips have built-in DSP modules to directly analyze audio signals and control the boost converter to adjust the voltage without external MCU intervention.
3. Optimization of low power consumption and thermal management
Reduced heat loss: Dynamic voltage significantly reduces transistor power consumption (P=Vce×Ic), and the size of the heat sink can be reduced by 30%-50%.
Improved power efficiency: The boost converter only provides high voltage when needed, enters low power mode when lightly loaded, and reduces system standby power consumption.
EMI suppression: By optimizing the switching frequency and filtering design, the high-frequency noise introduced by power switching is reduced to ensure pure sound quality.
4. Application scenarios and performance comparison
Compared with Class AB: Class H improves efficiency by more than 30% at medium power, but the circuit complexity is higher and the cost is increased.
Compared with Class D: Class H retains the sound quality advantage of linear amplifiers (low distortion), but the efficiency is slightly lower than Class D (more than 90%), which is suitable for high-fidelity systems with strict requirements on sound quality.
5. Typical applications:
Car audio: TI's reference design shows that the Class H solution can reduce PCB heat load and extend battery life.
Professional audio: The power amplifier achieves high output and low heat through Class H technology.

 English
English Español
Español 中文简体
中文简体