Using a Class-H speaker amplifier requires a full understanding of the working principle of its dynamic switching of multiple voltage rails and optimizing the configuration based on the actual needs of the audio system. The following is a professional-level operation guide covering connection, setup, protection and performance optimization:
1. System connection and initialization
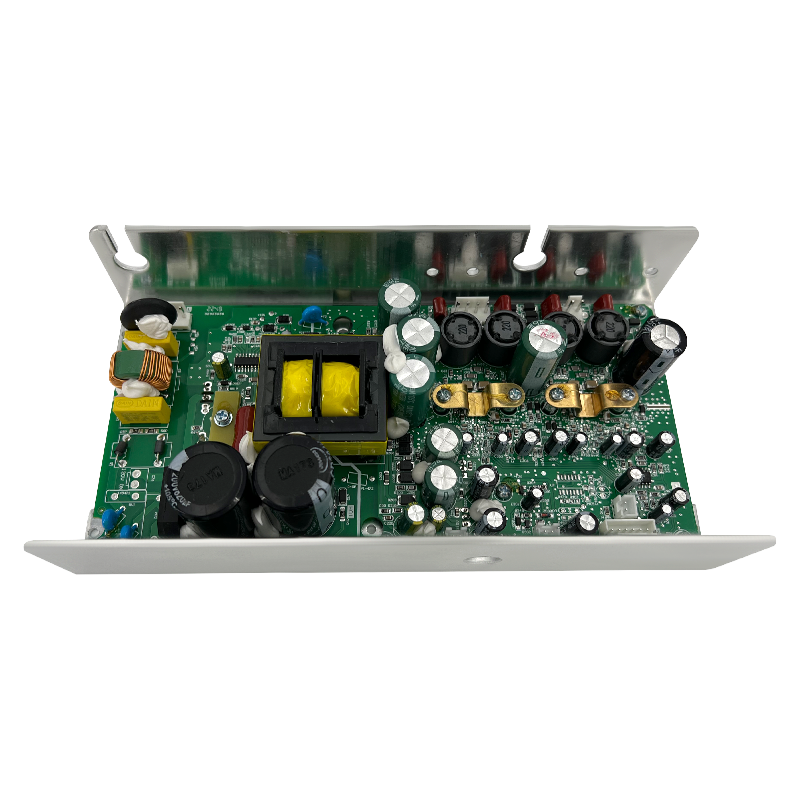
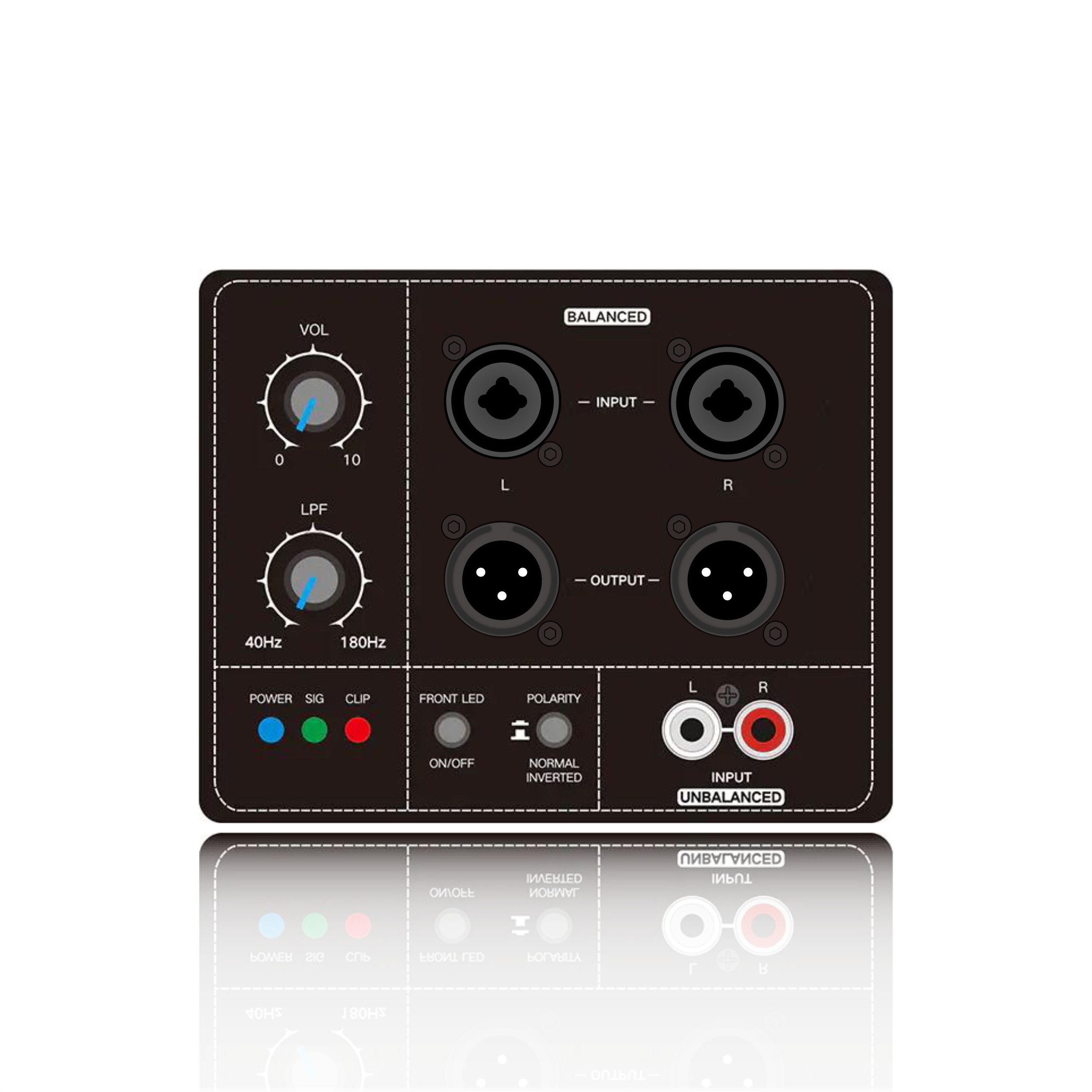
(1). Power supply configuration
Dual voltage rail access: Connect the main high voltage rail (±Vhigh, such as ±80V) and the auxiliary low voltage rail (±Vlow, such as ±40V), ensuring the correct polarity.
Use a fast recovery diode (such as FR307) to prevent voltage kickback, and the power supply internal resistance must be less than 0.1Ω to avoid switching transient drop.
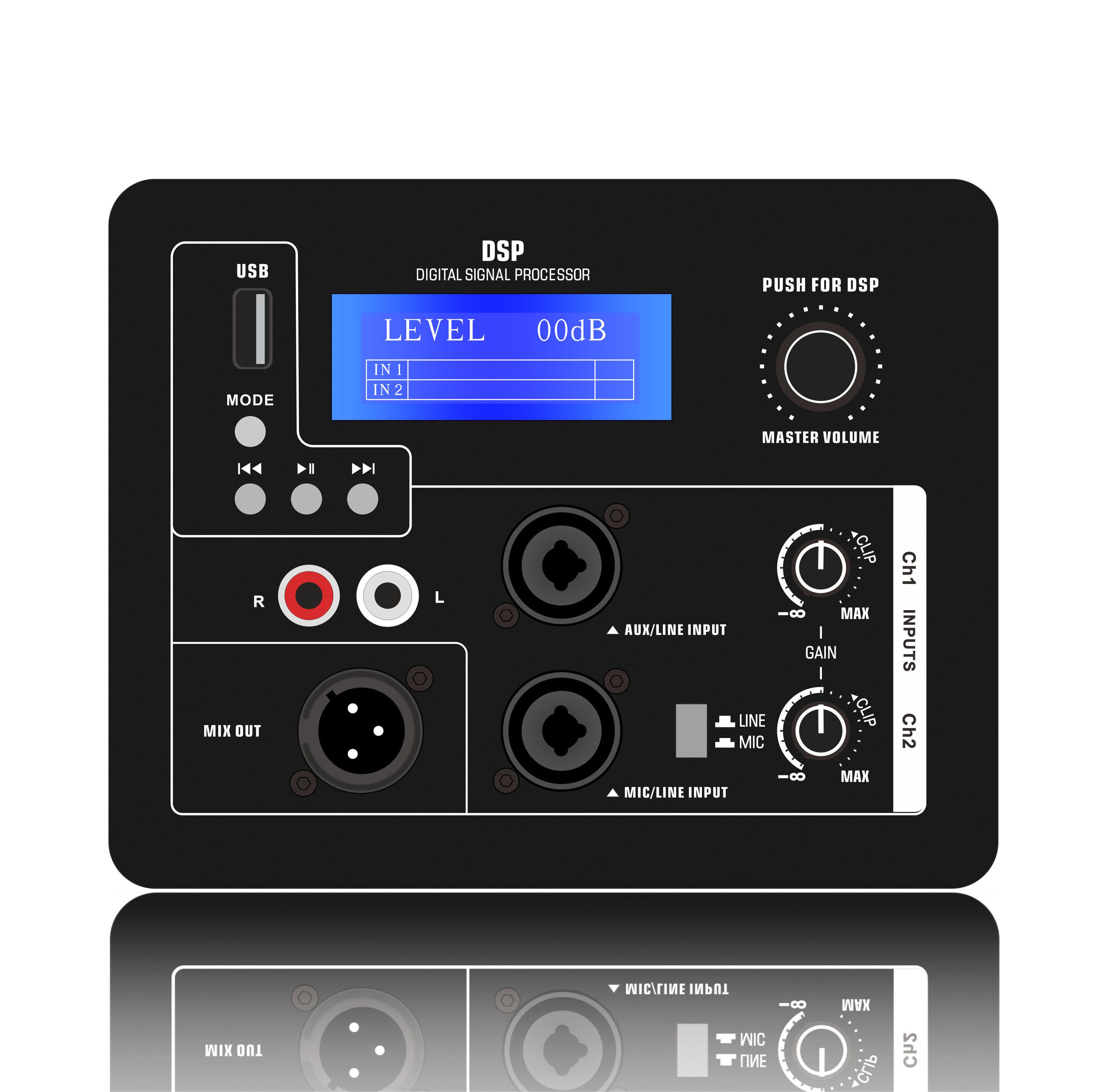
(2). Signal input
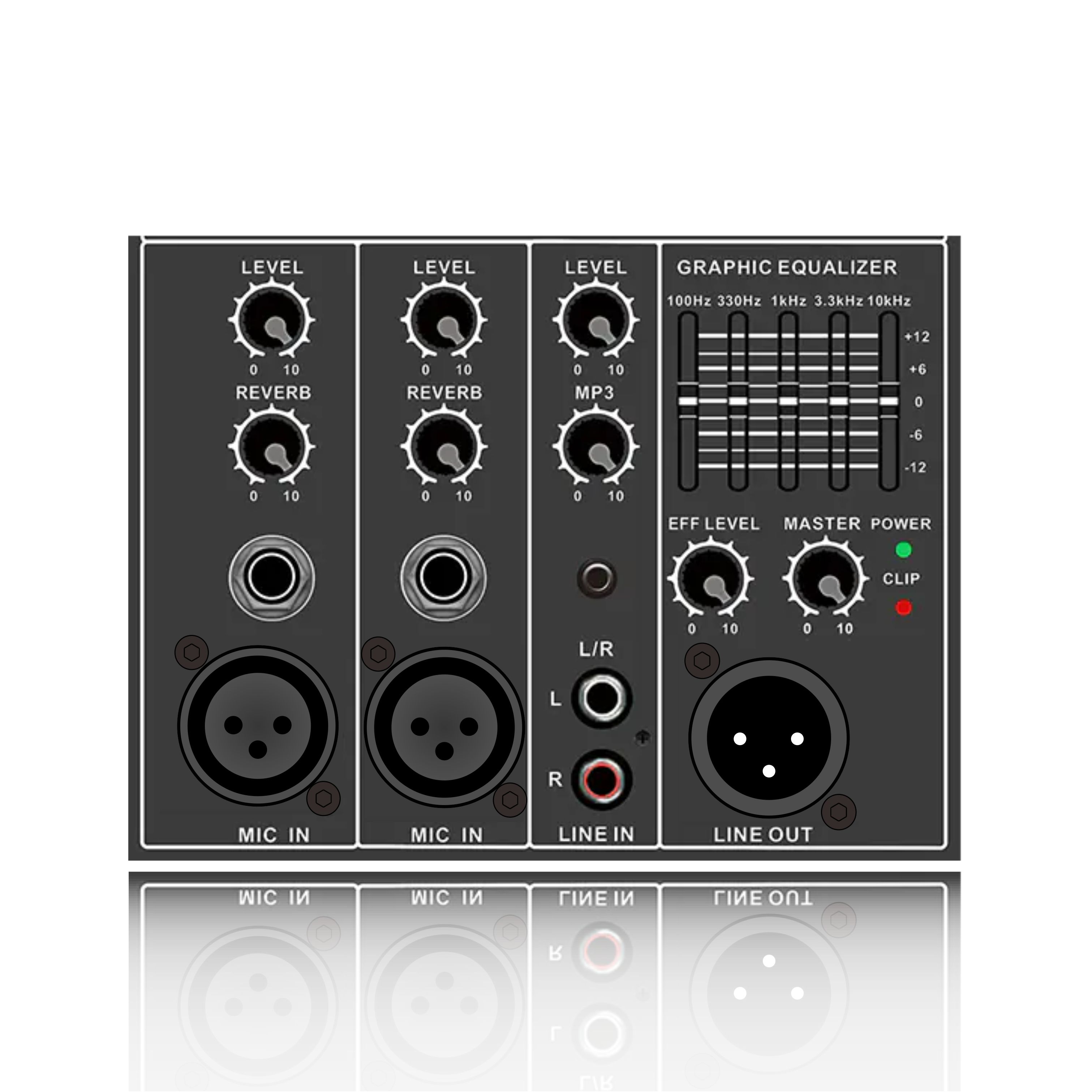
Input matching: When using a balanced input (XLR/TRS), the impedance must be matched (typically 10kΩ).
For single-ended input (RCA), it is recommended to add a buffer (such as OPA1632) to suppress common-mode noise.
(3). Load connection
Speaker impedance verification: Use an LCR meter to measure the actual speaker impedance (e.g., a nominal 8Ω speaker may drop to 4Ω at low frequencies).
Ensure that the load is ≥ the amplifier's nominal minimum impedance (e.g., 4Ω) to avoid triggering overcurrent protection.
2. Dynamic performance optimization
(1). Transient response enhancement
Gate drive adjustment: If switching transient ringing is found, add a resistor (Rg) in series with the MOSFET gate and an accelerating diode (e.g., 1N4148) in parallel:
Typical value: Rg = 10Ω~47Ω, diode reverse withstand voltage ≥ Vhigh.
(2). Frequency response compensation
High frequency extension: Test the 20kHz square wave response. If overshoot occurs, reduce the Miller compensation capacitor (Cc) or increase the output inductor (e.g., 1μH air core inductor).
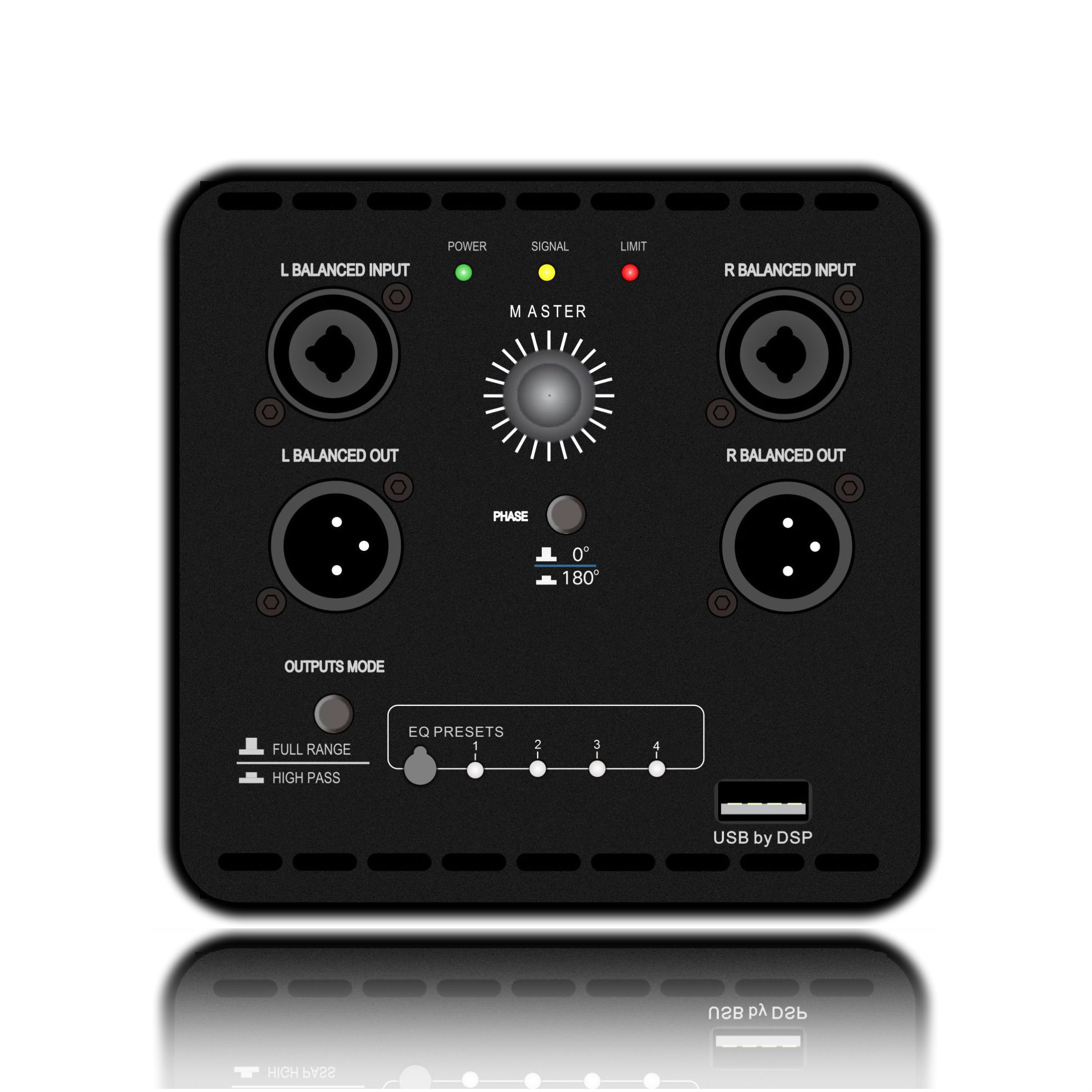
3. Protection function verification
(1). Overload test
Short-term overpower
Input 1kHz sine wave and gradually increase it to 120% of rated power. Verify that:
The current limiting circuit operates within 5 seconds (such as triggering clipping or reducing gain).
The heat sink temperature is less than 85℃ (forced air cooling requires the fan to be started).
(2). Fault simulation
Load short circuit
Short-circuit the output terminal for 2 seconds to confirm the protection circuit:
Immediately cut off the output and light up the fault indicator.
A manual reset is required (to avoid repeated shocks caused by automatic recovery).
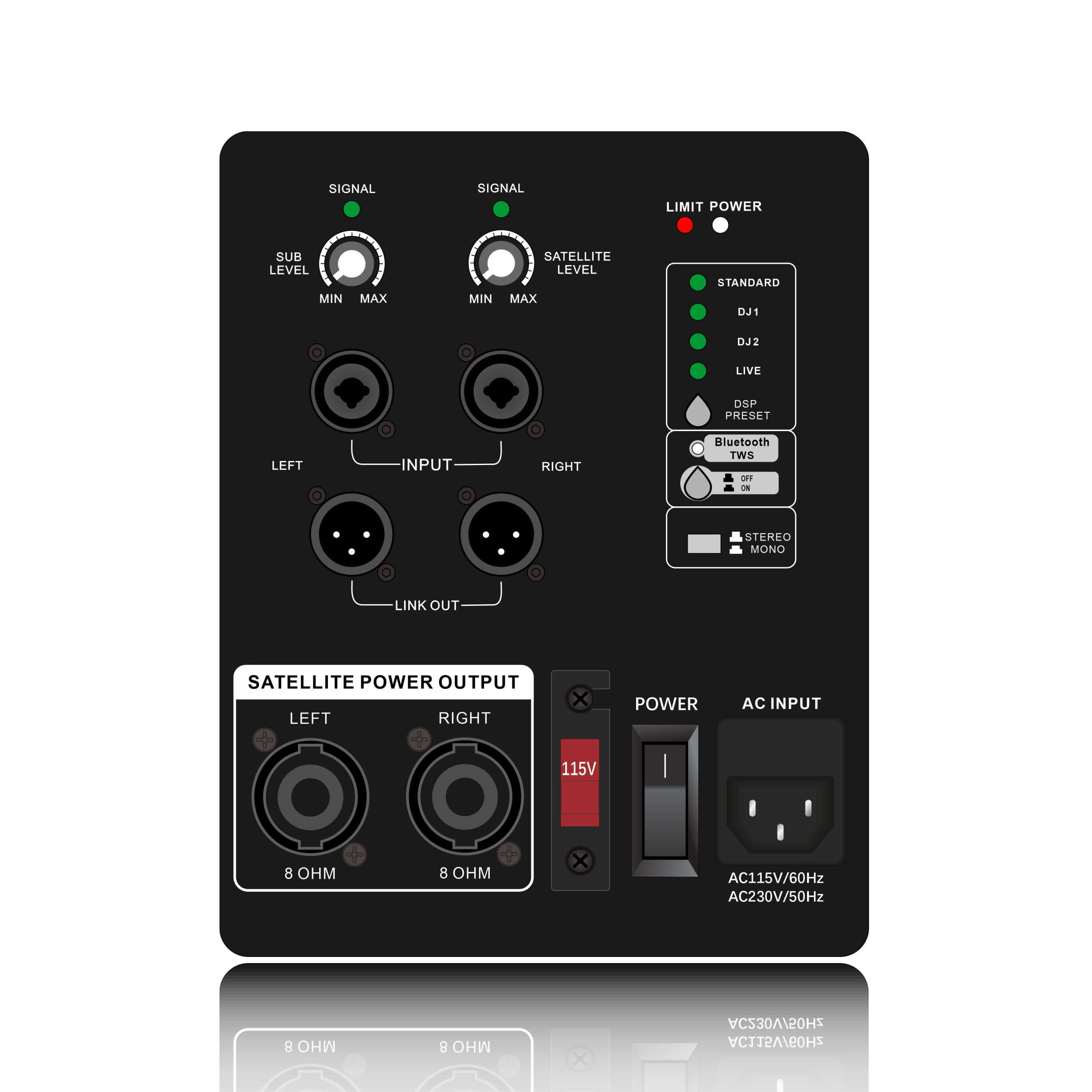
4. Maintenance and monitoring
(1). Regular inspection
Contact resistance measurement
Check the resistance of the speaker terminal and the PCB solder joint every quarter (should be less than 0.5Ω). Oxidized contact points need to be cleaned with DeoxIT.
(2). Performance degradation diagnosis
Efficiency monitoring
Compare the input power (AC end) with the output power (speaker end). When the efficiency drops by more than 10%, check whether the power tube on-resistance (Rds(on)) increases.
Replace the electrolytic capacitor (especially the bootstrap capacitor).

 English
English Español
Español 中文简体
中文简体